Artificial Intelligence (AI) has undergone significant transformations in recent decades, from rule-based systems to generative and agentic AI. This evolution is driven by advancements in computational power, data availability, and machine learning techniques. The transition from traditional AI to generative AI and finally to agentic AI systems is a continuous process.
Traditional AI: Era of Automation.
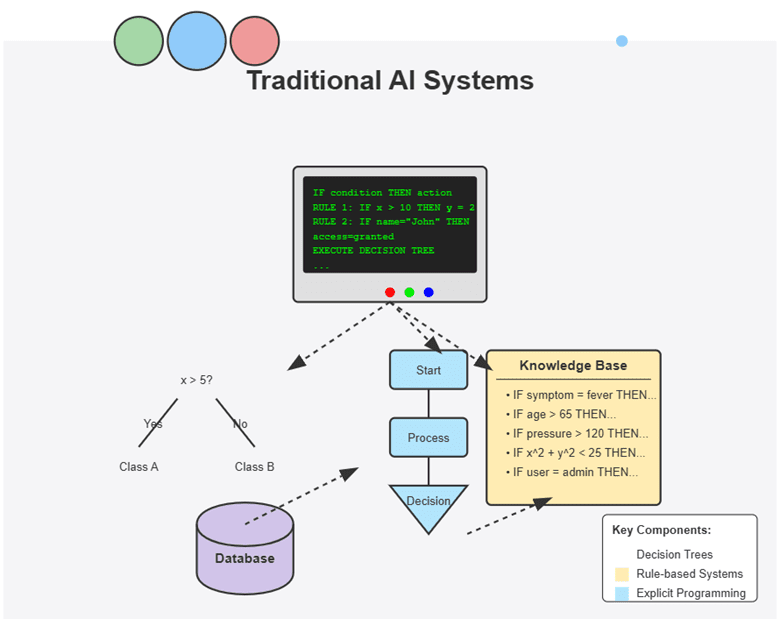
Traditionally, artificial intelligence was primarily focused on automation, with rule-based systems being the norm. Traditional AI, also known as narrow AI, involves programming machines for specific tasks using inference rules. Traditional AI systems use predefined rules, statistical models, and supervised learning algorithms to perform specific tasks. They are excellent at finding patterns, sorting them into groups, and improving performance in certain areas. Narrow AI is task-specific, which connotes that they can be used for singular tasks such as chess engines, spam filters, expert systems, fraud detection etc. In addition, narrow AI has predictable outputs and requires labeled data for training. While traditional AI systems lay the foundation for modern AI systems, they are limited because of their lack of flexibility, creativity, and dependence on labeled data. The future requires AI to adapt and learn on its own.
Generative AI: Era of Creativity
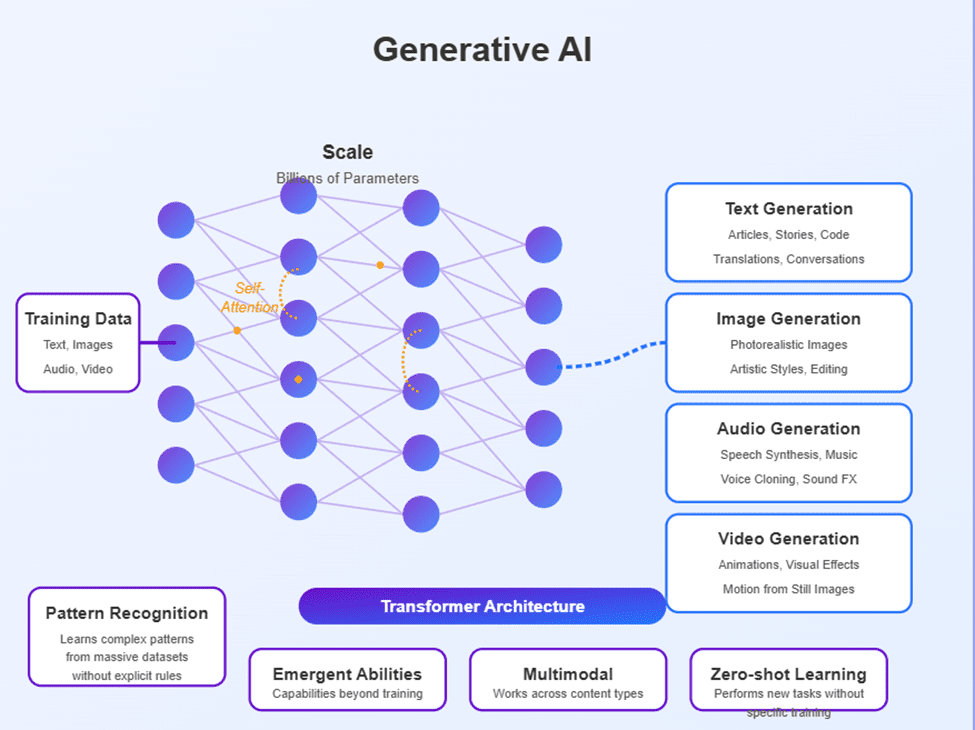
Advancements in technology have led to the emergence of data-driven AI, which enhances the intelligence and creativity of AI systems by training them with vast amounts of data. Gen AI, as popularly called, unlike traditional AI systems, can generate new data after being trained on existing datasets, allowing it to produce novel content and ideas. This capability not only broadens the scope of applications for AI but also enables it to solve complex problems in innovative ways, stimulating advancements across various fields. Gen AI’s ability to generate new content marks a significant advancement from narrow-based systems that rely solely on programming. This shift opens up endless possibilities across various fields, from art and music to scientific research and content creation. As generative AI continues to evolve, it has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach problem solving and innovation.
Instead of depending on predetermined rules, Gen AI uses machine learning algorithms to discover connections, patterns, and insights from giant volumes of data. As a strong paradigm, machine learning grew over time. It used algorithms like decision trees, support vector machines, and neural networks to make predictions, classifications, and suggestions based on data. Deep learning arose as an area in machine learning in the 2010s, owing to advances in neural networks with several layers (hence the name). Deep learning permitted important advancements, particularly in computer vision (image and video identification), voice recognition, and natural language processing (NLP). Gen AI uses self-supervised learning and deep learning and instead of relying on predefined data, the AI trains itself on vast amounts of data.
Gen-AI is therefore used in several applications, e.g., generating text, video, codes, and voice recognition; text-to-speech, etc.; used for automating business content, automating gaming, personalization (chatbots and virtual assistants), etc.
Agentic AI: Era of Autonomy
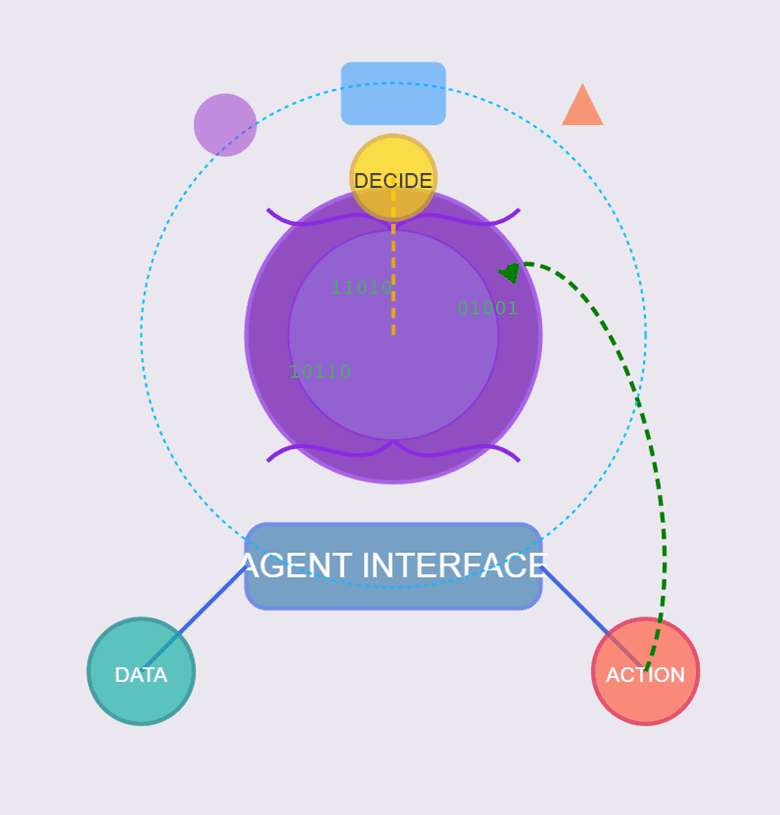
AI agents refer to environmentally aware systems that are capable of making decisions. Agentic AI is a type of autonomous system that combines Gen AI’s creativity with decision-making frameworks, planning, iterating, and interacting with environments or users without constant human input. Agentic AI broadens the scope of AI beyond its ability to generate new items, enabling it to act autonomously. Agentic systems are goal-orientated, operate with a defined objective, can self-improve by learning from feedback, and use different means, such as text, voice, and APIs, to execute tasks.
Agentic AIs are autonomous; they can plan, utilise tools, retain memory, improve based on feedback, and be aware of their environment. Autonomy means being able to do things on your own with little or no help; planning means making detailed plans, knowing how to use tools correctly, and keeping your memory sharp so you can remember what happened or what you did in the past; self-improvement means judging your own performance based on results; and environmental awareness means being able to adapt to new situations. These skills are crucial for success in various fields.
Agentic systems have advanced use cases, such as AI assistants that perform actions; research agents that can summarise research papers; robotics; DevOps agents; and healthcare agents.
Implications of Agentic Systems
The advancement of AI agents has significant implications for technological, economic, and social aspects. Agentic AI offers unprecedented productivity gains by automating complex workflows, extending beyond routine tasks to creative and knowledge work. This raises questions about employment and economic organisation. As AI systems become more agentic, they become active partners in problem-solving, potentially amplifying human capabilities while challenging traditional work structures. However, this process also brings increased responsibility for ensuring AI systems remain aligned with human values and intentions. Existing frameworks designed for traditional software systems or generative models make regulatory considerations crucial. The transition from traditional AI to agentic systems represents a fundamental reimagining of the relationship between humans and machines. Principles for navigating this transition include responsible development, inclusive benefits, human-centered design, adaptive governance, and ongoing research. The choices made about developing, deploying, and governing agentic AI will shape the future of technology and human society.








